개요
Mechanical vibration — Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non-rotating parts —
Part 3:
Industrial machines with nominal power above 15 kW and nominal speeds between 120 r/min and 15 000 r/min when measured in situ
기계적 진동 — 비회전부의 측정에 의한 기계 진동의 평가 —
제3부:
현장에서 측정된 호칭 출력 15 kW 초과 및 호칭 속도 120 r/min∼15 000 r/min인 산업용 기계
이 표준은 현장에서 측정된 진동 수준을 평가하는 기준을 제공한다. 제시된 진동 기준은 출력이 15 kW를 초과하고 120 r/min∼15 000 r/min 사이의 속도로 운전하는 기계 세트에 적용한다.
이 표준에 적용되는 기계는 다음과 같다.
- Steam turbines with power up to 50 MW; (출력 50MW 이하의 증기 터빈)
- Steam turbine sets with power greater than 50 MW and speeds below 1 500 r/min or above 3 600 r/min (not included in ISO 10816-2); (출력 50MW를 초과하고, 1500r/min 미만 또는 3600r/min을 초과하는 속도로 운전하는 증기터빈 (ISO 10816-2에 포함되지 않는 것))
- Rotary compressors; (회전 압축기)
- Industrial gas turbines with power up to 3 MW; (출력 3MW 이하의 산업용 가스 터빈)
- Generators; (발전기)
- Electrical motors of any type; (모든 종류의 전기 모터)
- Blowers or fans. (송풍기 혹은 팬)
측정위치
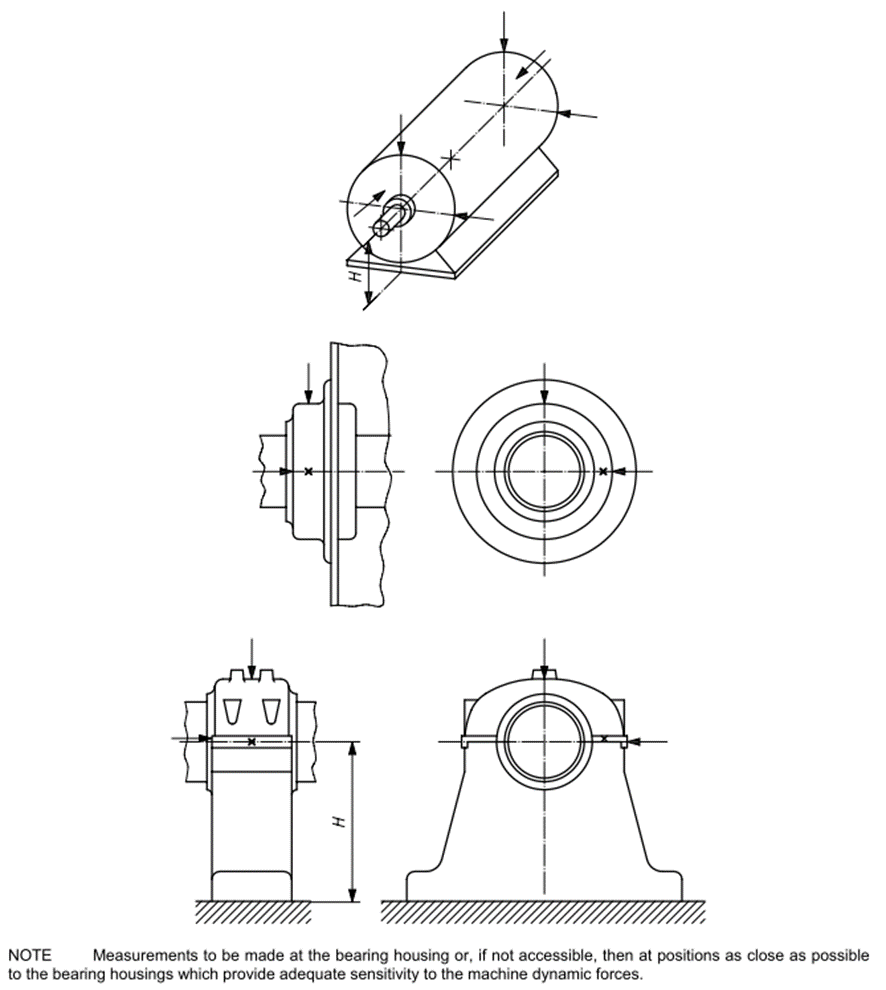

진동평가


지지 유연성에 따른 구분
Two conditions are used to classify the support assembly flexibility in specified directions:
⎯ rigid supports;
⎯ flexible supports.
These support conditions are determined by the relationship between the machine and foundation flexibilities. If the lowest natural frequency of the combined machine and support system in the direction of measurement is higher than its main excitation frequency (this is in most cases the rotational frequency) by at least 25 %, then the support system may be considered rigid in that direction. All other support systems may be considered flexible.
측정방향에서 최저 고유진동수가 주 가진 주파수보다 최소 25% 이상 크다면 이 지지시스템은 그 방향으로 Rigid (강성)하다고 할 수 있다. 그 외의 다른 모든 지지 시스템은 Flexible(유연)하다고 간주할 수 있다.
As typical examples, large and medium-sized electric motors, mainly with low speeds, would normally have rigid supports, whereas turbo-generators or compressors with power greater than 10 MW and vertical machine sets would usually have flexible supports.
In some cases, a support assembly may be rigid in one measuring direction and flexible in the other. For example, the lowest natural frequency in the vertical direction may be well above the main excitation frequency, while the horizontal natural frequency may be considerably less. Such a system would be stiff in the vertical plane but flexible in the horizontal. In such cases, the vibration should be evaluated in accordance with the support classification which corresponds to the measurement direction.
If the class of a machine-support system cannot be readily determined from drawings and calculation, it may be determined by testing.
기타
NEMA MG-1 "MOTORS AND GENERATORS"에 언급된 지지 구조
7.6 Machine Mounting
7.6.1 General
Evaluation of vibration of rotating electrical machines requires measurement of the machines
under properly determined test conditions to enable reproducible tests and to provide comparable
measurements. The vibration of an electrical machine is closely linked with the mounting of the machine.
The choice of the mounting method will be made by the manufacturer. Typically, machines with shaft
heights of 11 inches or less use resilient mounting. For machines with speeds lower than 600 rpm,
resilient mounting is not practical.
NOTE: The shaft height of a machine without feet, or a machine with raised feet, or any vertical machine, is to be taken as the shaft height of a machine in the same basic frame, but of the horizontal shaft foot mounting type.
7.6.2 Resilient Mounting
Resilient mounting is achieved by suspending the machine on a spring or by mounting it on an elastic
support (springs, rubber, etc.).
The vertical natural oscillation frequency of the suspension system and machine should be less than
33 percent of the frequency corresponding to the lowest speed of the machine under test, as defined in 7.7.3.3. For an easy determination of the necessary elasticity of the suspension system, see Figure 7-1.
The effective mass of the elastic support shall be no greater than 10 percent of that of the machine, to reduce the influence of the mass and the moments of inertia of these parts on the vibration level.
7.6.3 Rigid Mounting
Rigid mounting is achieved by fastening the machine directly to a massive foundation.
A massive foundation is one that has a vibration (in any direction or plane) limited, during testing, to 0.02
in/s peak (0.5 mm/s peak) above any background vibrations. The natural frequencies of the foundation
should not coincide within ±10 percent of the rotational frequency of the machine, within ±5 percent of two times rotational frequency, or within ±5 percent of one- and two-times electrical-line frequency.
The vibration velocity of the foundation in the horizontal and vertical directions near the machine feet
should not exceed 25 percent of the maximum velocity at the adjacent bearing in either the horizontal or
vertical direction at rotational frequency and at twice line frequency (if the latter is being evaluated).
'Codes & Standards' 카테고리의 다른 글
| API 610_Centrifugal Pumps for Petroleum, Petrochemical, and Natural Gas Industries (1) | 2025.02.04 |
|---|---|
| ISO 10816-7 (1st Edition, 2009) 회전동역학 펌프의 진동 평가) (0) | 2021.07.21 |

